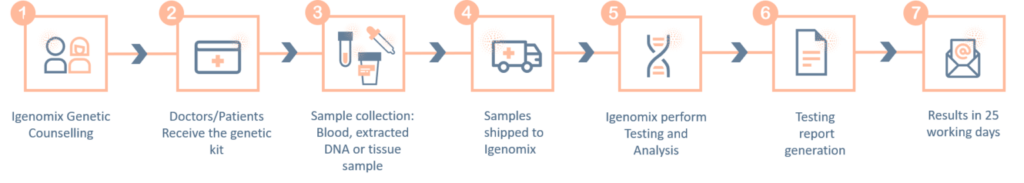
Congenital Muscular Dystrophies and Myopathies Precision Panel
Congenital Muscular Dystrophies are an inherited group of progressive myopathic disorders resulting from defects in a number of genes responsible for normal muscle function, resulting in progressive muscle weakness without a central or peripheral nerve abnormality.